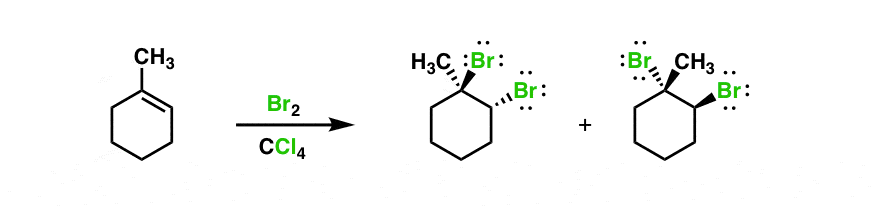
 Halogenation of alkenes is an example of a stereoselective reaction. The reaction of Br 2, Cl 2 and other halogens with alkenes leads to products of anti – addition.
Halogenation of alkenes is an example of a stereoselective reaction. The reaction of Br 2, Cl 2 and other halogens with alkenes leads to products of anti – addition.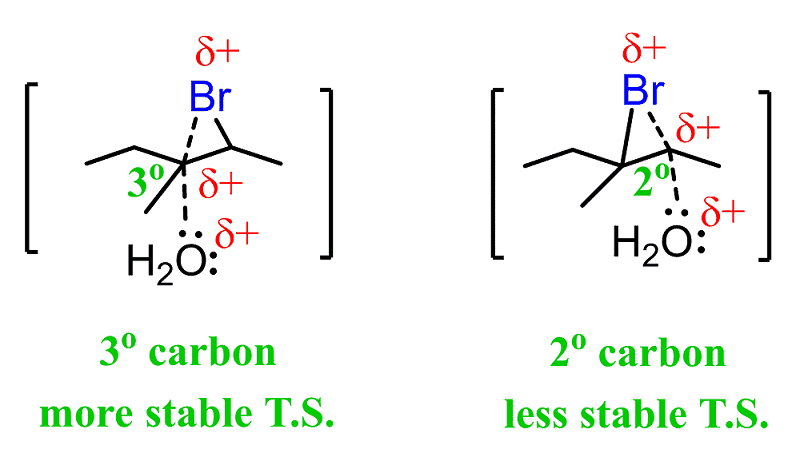 Draw a mechanism for each reaction to explain the difference when the following alkenes are reacted with bromine. Hint: drawing the chair conformations will be very helpful.
Draw a mechanism for each reaction to explain the difference when the following alkenes are reacted with bromine. Hint: drawing the chair conformations will be very helpful.